本文基于对 Kubernetes v1.23.1 的源码阅读
Kubernetes 提供了一种 Pod 优雅退出机制,使 Pod 在退出前可以完成一些清理工作。但若执行清理工作时出错了,Pod 能正常退出吗?多久能退出?退出时间可以指定吗?系统有默认参数吗?这其中有若干细节值得我们去注意,本文就从这些细节出发,梳理清楚每种情况下 Kubernetes 的组件的各项行为及其参数设定。
Pod 正常退出
Pod 正常退出是指非被驱逐时退出,包括人为删除、执行出错被删除等。在 Pod 退出时,kubelet 删除容器之前,会先执行 pod 的 preStop,允许 pod 在退出前执行一段脚本用以清除必要的资源等。然而 preStop 也有执行失败或者直接 hang 住的情况,这个时候 preStop 并不会阻止 pod 的退出,kubelet 也不会重复执行,而是会等一段时间,超过这个时间会直接删除容器,保证整个系统的稳定。
整个过程在函数 killContainer 中,我们在 pod 优雅退出时,需要明确的是,kubelet 的等待时间由那几个因素决定,用户可以设置的字段和系统组件的参数是如何共同作用的。
gracePeriod
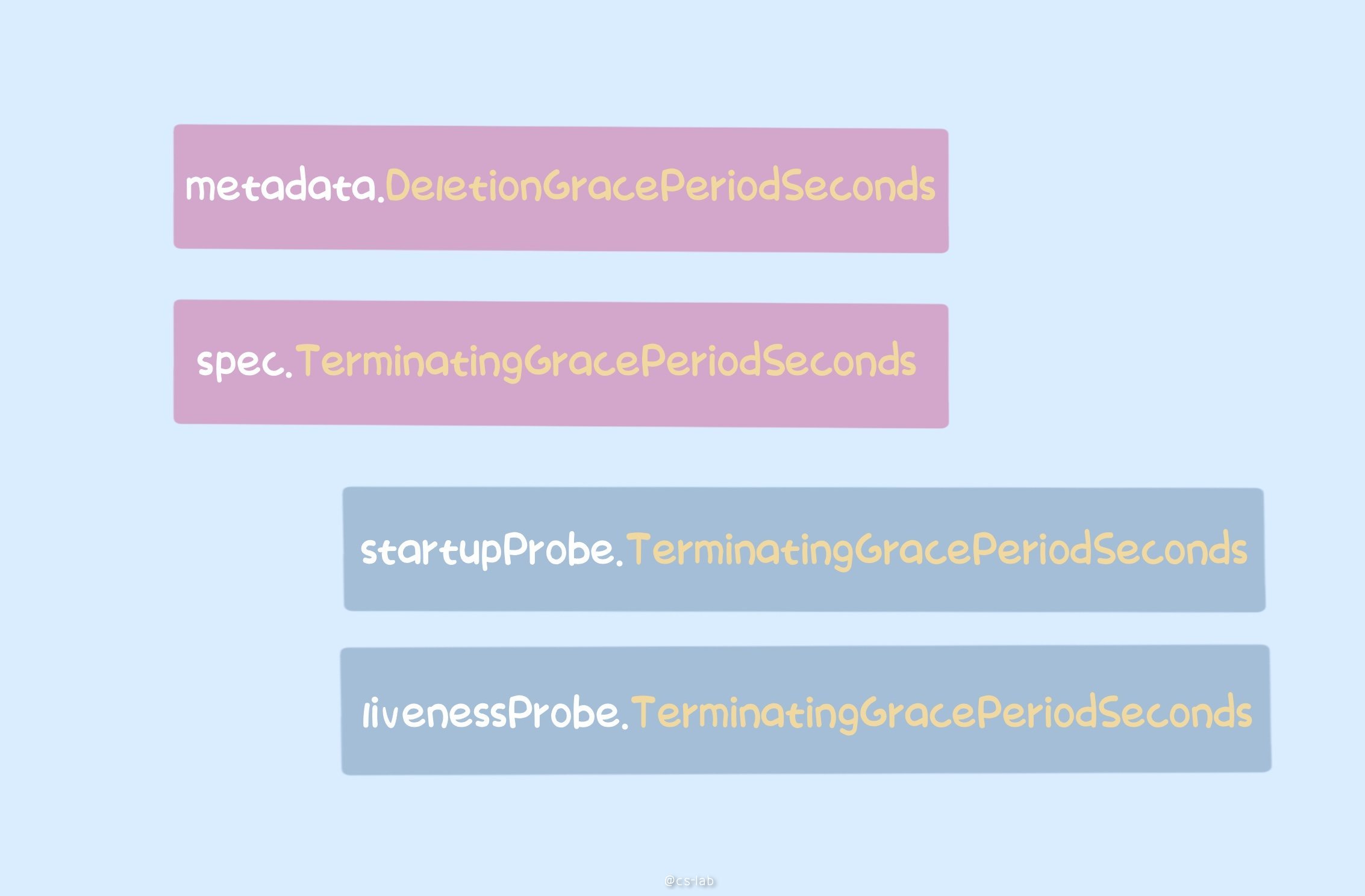
kubelet 计算 gracePeriod 的过程为:
- 如果 pod 的
DeletionGracePeriodSeconds不为 nil,表示是 ApiServer 删除的,gracePeriod 直接取值; - 如果 pod 的
Spec.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds不为 nil,再看 pod 删除的原因是什么;- 若删除原因为执行
startupProbe失败,gracePeriod 取值为startupProbe中设置的TerminationGracePeriodSeconds - 若删除原因为执行
livenessProbe失败,gracePeriod 取值为livenessProbe中设置的TerminationGracePeriodSeconds
- 若删除原因为执行
获得到 gracePeriod 之后,kubelet 执行 pod 的 preStop,函数 executePreStopHook 中会起一个 goroutine ,并计算其执行的时间,gracePeriod 再减去该时间,就是最终传给 runtime 的删除容器的 timeout 时间。所以,若我们设置了 pod preStop,需要同时考虑到 preStop 的执行时间以及容器退出的时间,可以给 TerminationGracePeriodSeconds 设置一个大于 preStop + 容器退出的时间。
func (m *kubeGenericRuntimeManager) killContainer(pod *v1.Pod, containerID kubecontainer.ContainerID, containerName string, message string, reason containerKillReason, gracePeriodOverride *int64) error {
...
// From this point, pod and container must be non-nil.
gracePeriod := int64(minimumGracePeriodInSeconds)
switch {
case pod.DeletionGracePeriodSeconds != nil:
gracePeriod = *pod.DeletionGracePeriodSeconds
case pod.Spec.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds != nil:
gracePeriod = *pod.Spec.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds
switch reason {
case reasonStartupProbe:
if containerSpec.StartupProbe != nil && containerSpec.StartupProbe.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds != nil {
gracePeriod = *containerSpec.StartupProbe.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds
}
case reasonLivenessProbe:
if containerSpec.LivenessProbe != nil && containerSpec.LivenessProbe.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds != nil {
gracePeriod = *containerSpec.LivenessProbe.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds
}
}
}
// Run internal pre-stop lifecycle hook
if err := m.internalLifecycle.PreStopContainer(containerID.ID); err != nil {
return err
}
// Run the pre-stop lifecycle hooks if applicable and if there is enough time to run it
if containerSpec.Lifecycle != nil && containerSpec.Lifecycle.PreStop != nil && gracePeriod > 0 {
gracePeriod = gracePeriod - m.executePreStopHook(pod, containerID, containerSpec, gracePeriod)
}
// always give containers a minimal shutdown window to avoid unnecessary SIGKILLs
if gracePeriod < minimumGracePeriodInSeconds {
gracePeriod = minimumGracePeriodInSeconds
}
if gracePeriodOverride != nil {
gracePeriod = *gracePeriodOverride
}
err := m.runtimeService.StopContainer(containerID.ID, gracePeriod)
...
return nil
}
gracePeriodOverride
在上面分析的过程中,kubelet 调用 runtime 接口之前,会再判断一步 gracePeriodOverride,若传进来的值不为空,直接用该值覆盖前面的 gracePeriod。

kubelet 计算 gracePeriodOverride 的主要过程如下:
- 取值 pod 的
DeletionGracePeriodSeconds; - 若 kubelet 是在驱逐 pod,则用驱逐的设置 pod 退出时间覆盖;
func calculateEffectiveGracePeriod(status *podSyncStatus, pod *v1.Pod, options *KillPodOptions) (int64, bool) {
gracePeriod := status.gracePeriod
// this value is bedrock truth - the apiserver owns telling us this value calculated by apiserver
if override := pod.DeletionGracePeriodSeconds; override != nil {
if gracePeriod == 0 || *override < gracePeriod {
gracePeriod = *override
}
}
// we allow other parts of the kubelet (namely eviction) to request this pod be terminated faster
if options != nil {
if override := options.PodTerminationGracePeriodSecondsOverride; override != nil {
if gracePeriod == 0 || *override < gracePeriod {
gracePeriod = *override
}
}
}
// make a best effort to default this value to the pod's desired intent, in the event
// the kubelet provided no requested value (graceful termination?)
if gracePeriod == 0 && pod.Spec.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds != nil {
gracePeriod = *pod.Spec.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds
}
// no matter what, we always supply a grace period of 1
if gracePeriod < 1 {
gracePeriod = 1
}
return gracePeriod, status.gracePeriod != 0 && status.gracePeriod != gracePeriod
}
ApiServer 的行为
在上面分析 kubelet 处理 pod 的退出时间时,我们会发现 kubelet 会首先用 pod 的 DeletionGracePeriodSeconds,而该值正是 ApiServer 删除 pod 时写入的。本节我们来分析 ApiServer 删除 pod 时的行为。
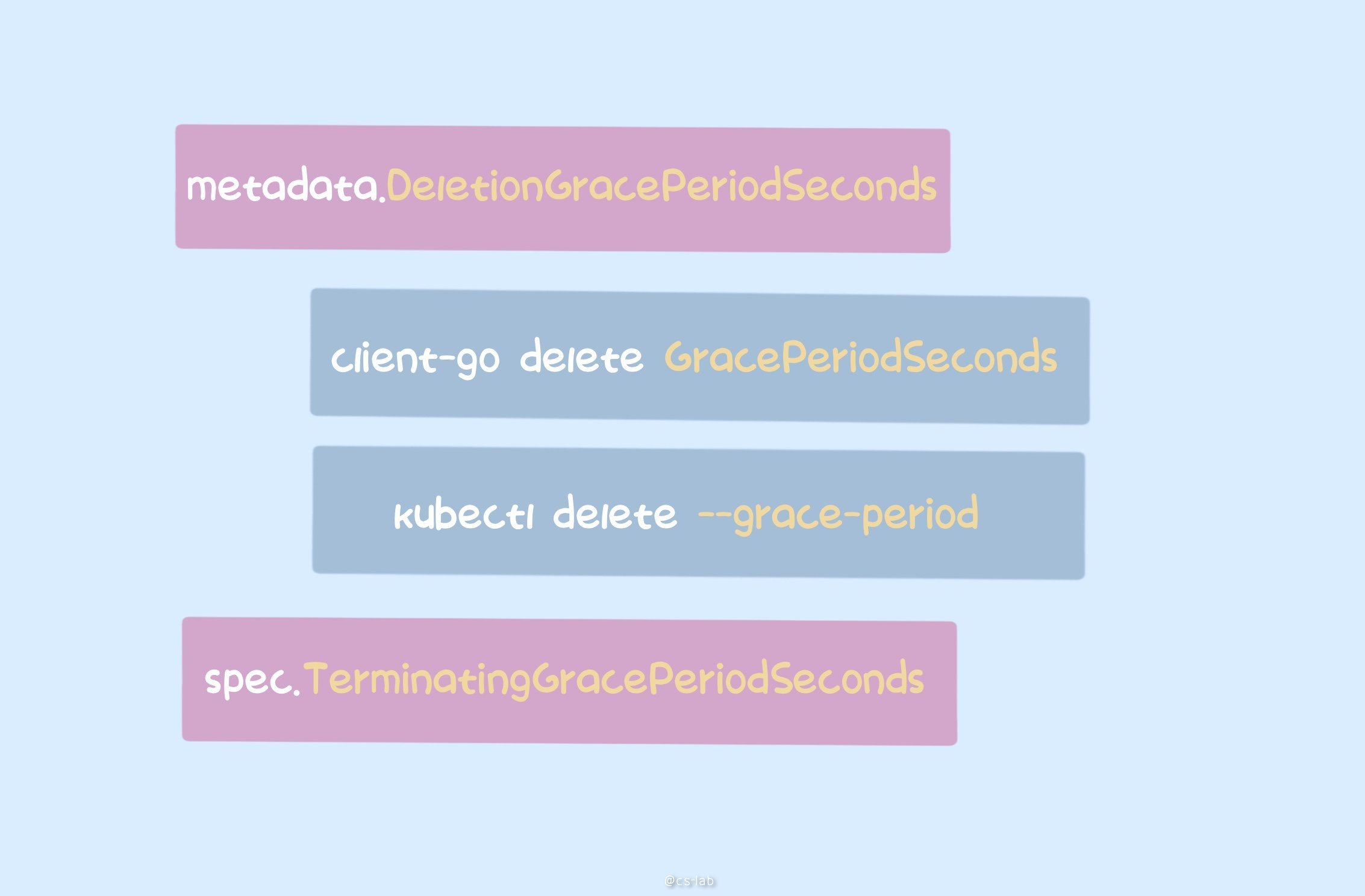
ApiServer 中计算 pod 的 GracePeriodSeconds 过程为:
- 若
options.GracePeriodSeconds不为空,则设置为该值;否则设置为 spec 中用户指定的Spec.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds(默认为 30s); - 若 pod 未被调度或已经退出,则设置为 0,即立即删除;
其中,options.GracePeriodSeconds 为 kubectl 删除 pod 时,可以指定的参数 --grace-period;或者程序里调用 ApiServer 接口时指定的参数,如 client-go 中的 DeleteOptions.GracePeriodSeconds。
func (podStrategy) CheckGracefulDelete(ctx context.Context, obj runtime.Object, options *metav1.DeleteOptions) bool {
if options == nil {
return false
}
pod := obj.(*api.Pod)
period := int64(0)
// user has specified a value
if options.GracePeriodSeconds != nil {
period = *options.GracePeriodSeconds
} else {
// use the default value if set, or deletes the pod immediately (0)
if pod.Spec.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds != nil {
period = *pod.Spec.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds
}
}
// if the pod is not scheduled, delete immediately
if len(pod.Spec.NodeName) == 0 {
period = 0
}
// if the pod is already terminated, delete immediately
if pod.Status.Phase == api.PodFailed || pod.Status.Phase == api.PodSucceeded {
period = 0
}
if period < 0 {
period = 1
}
// ensure the options and the pod are in sync
options.GracePeriodSeconds = &period
return true
}
kubelet 驱逐 pod
另外,在 kubelet 驱逐 pod 时,pod 的优雅退出时间是被覆盖的。

func (m *managerImpl) synchronize(diskInfoProvider DiskInfoProvider, podFunc ActivePodsFunc) []*v1.Pod {
...
// we kill at most a single pod during each eviction interval
for i := range activePods {
pod := activePods[i]
gracePeriodOverride := int64(0)
if !isHardEvictionThreshold(thresholdToReclaim) {
gracePeriodOverride = m.config.MaxPodGracePeriodSeconds
}
message, annotations := evictionMessage(resourceToReclaim, pod, statsFunc)
if m.evictPod(pod, gracePeriodOverride, message, annotations) {
metrics.Evictions.WithLabelValues(string(thresholdToReclaim.Signal)).Inc()
return []*v1.Pod{pod}
}
}
...
}
其 override 值为 EvictionMaxPodGracePeriod,且只有软驱逐时有效,该值为 kubelet 的驱逐相关的配置参数:
// Map of signal names to quantities that defines hard eviction thresholds. For example: {"memory.available": "300Mi"}.
EvictionHard map[string]string
// Map of signal names to quantities that defines soft eviction thresholds. For example: {"memory.available": "300Mi"}.
EvictionSoft map[string]string
// Map of signal names to quantities that defines grace periods for each soft eviction signal. For example: {"memory.available": "30s"}.
EvictionSoftGracePeriod map[string]string
// Duration for which the kubelet has to wait before transitioning out of an eviction pressure condition.
EvictionPressureTransitionPeriod metav1.Duration
// Maximum allowed grace period (in seconds) to use when terminating pods in response to a soft eviction threshold being met.
EvictionMaxPodGracePeriod int32
kubelet 驱逐 pod 的函数是启动时注入的,函数如下:
func killPodNow(podWorkers PodWorkers, recorder record.EventRecorder) eviction.KillPodFunc {
return func(pod *v1.Pod, isEvicted bool, gracePeriodOverride *int64, statusFn func(*v1.PodStatus)) error {
// determine the grace period to use when killing the pod
gracePeriod := int64(0)
if gracePeriodOverride != nil {
gracePeriod = *gracePeriodOverride
} else if pod.Spec.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds != nil {
gracePeriod = *pod.Spec.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds
}
// we timeout and return an error if we don't get a callback within a reasonable time.
// the default timeout is relative to the grace period (we settle on 10s to wait for kubelet->runtime traffic to complete in sigkill)
timeout := int64(gracePeriod + (gracePeriod / 2))
minTimeout := int64(10)
if timeout < minTimeout {
timeout = minTimeout
}
timeoutDuration := time.Duration(timeout) * time.Second
// open a channel we block against until we get a result
ch := make(chan struct{}, 1)
podWorkers.UpdatePod(UpdatePodOptions{
Pod: pod,
UpdateType: kubetypes.SyncPodKill,
KillPodOptions: &KillPodOptions{
CompletedCh: ch,
Evict: isEvicted,
PodStatusFunc: statusFn,
PodTerminationGracePeriodSecondsOverride: gracePeriodOverride,
},
})
// wait for either a response, or a timeout
select {
case <-ch:
return nil
case <-time.After(timeoutDuration):
recorder.Eventf(pod, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.ExceededGracePeriod, "Container runtime did not kill the pod within specified grace period.")
return fmt.Errorf("timeout waiting to kill pod")
}
}
}
killPodNow 函数是 kubelet 在驱逐 pod 时所调用的函数,gracePeriodOverride 为软驱逐时设置的参数,当其没有设置时,gracePeriod 依然取值 pod.Spec.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds。然后该函数会调用 podWorkers.UpdatePod,传入相应参数,并且设置一个跟 gracePeriod 相关的超时时间,等待其返回。
总结
Pod 的优雅退出是由 preStop 实现的,本文就 Pod 正常退出和被驱逐时,Pod 的退出时间受哪些因素影响,各参数之间是如何相互作用的做了简要的分析。了解了这些细节后,我们对 Pod 的退出流程就有了一个更加全面的认知。